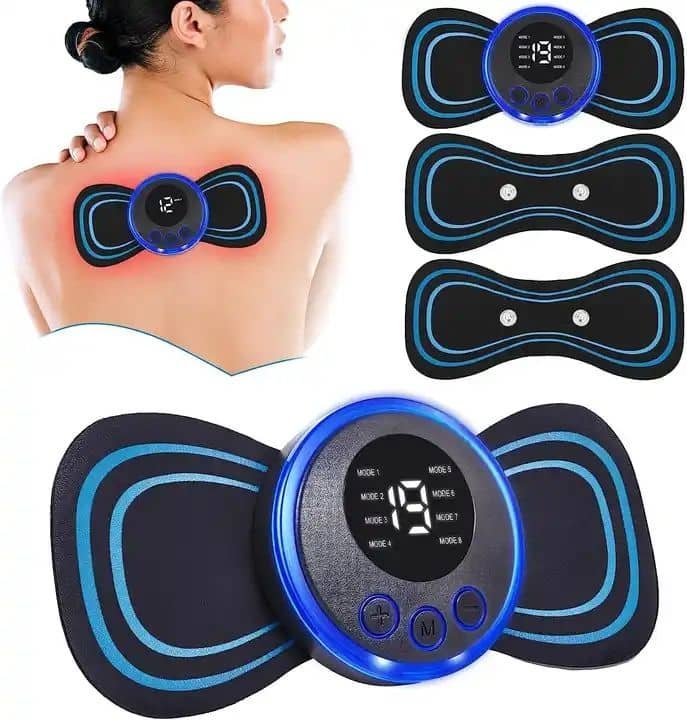
Are EMS Neck Massagers Safe? A Comprehensive Safety Analysis
The growing popularity of EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) neck massagers has raised important questions about their safety and appropriate usage. From portable neck massager devices to sophisticated smart neck massager systems, consumers are increasingly turning to these technological solutions for pain relief and muscle relaxation. But are EMS neck massagers safe, and what precautions should users take? This comprehensive examination addresses safety concerns, medical considerations, and proper usage guidelines for EMS technology.
Understanding EMS Technology and Its Applications
EMS devices use electrical impulses to stimulate muscle contractions, mimicking the natural signals from the nervous system. These impulses are delivered through electrodes placed on the skin, causing muscles to contract and relax. The technology comes in various forms:
Device Categories:
Portable electric neck massager: Compact, battery-operated units
Back and neck massager: Comprehensive systems for upper body use
EMS mini massager: Ultra-compact targeted devices
Intelligent neck massager: Programmable, adaptive systems
Electric massager for back pain: Multi-purpose therapeutic devices
Safety Mechanisms in Modern EMS Devices
Reputable manufacturers incorporate multiple safety features:
Built-in Safety Protocols:
Automatic shut-off timers (typically 15-30 minutes)
Intensity limiters to prevent overstimulation
Impulse frequency controls
Temperature monitoring systems
Low battery indicators
Quality Assurance Standards:
FDA clearance for medical devices
CE marking for European markets
ISO certification for manufacturing standards
Electrical safety certifications (UL, ETL)
General Safety Profile for Healthy Users
For most healthy adults, EMS devices are generally safe when used properly:
Appropriate Uses:
Muscle relaxation and tension relief
Temporary pain management
Exercise recovery support
Stress reduction and relaxation
Typical Sensations:
Mild tingling or buzzing feeling
Muscle twitching or contraction
Warmth in treatment area
Temporary redness under electrodes
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While generally safe, EMS devices can cause issues in certain circumstances:
Common Minor Side Effects:
Skin irritation from electrodes
Muscle soreness from overuse
Temporary redness or marks
Headache from tension release
Rare But Serious Risks:
Burn injuries from malfunctioning devices
Muscle damage from excessive intensity
Nerve irritation from improper placement
Heart rhythm issues in susceptible individuals
Medical Contraindications and Precautions
Absolute Contraindications:
Pacemakers or other implanted electronic devices
Pregnancy (particularly abdominal use)
Epilepsy or seizure disorders
Active cancer or recent radiation treatment
Deep vein thrombosis or blood clots
Relative Contraindications (Consult Doctor First):
Heart conditions or arrhythmias
Sensory disorders or neuropathy
Skin conditions or open wounds
Recent surgeries or injuries
High blood pressure
Device-Specific Safety Considerations
Portable Neck Massager Safety:
Ensure proper electrode placement
Avoid prolonged use on same area
Monitor battery levels regularly
Keep away from water despite portability
Electric Neck Massager Precautions:
Check cord integrity regularly
Use proper voltage adapters
Avoid use during electrical storms
Don’t use while charging unless designed for it
Smart Neck Massager Considerations:
Understand app permissions and data privacy
Keep software updated for safety patches
Be cautious with automated intensity adjustments
Monitor for technical glitches
Proper Usage Guidelines for Safety
Preparation Steps:
Read manufacturer instructions thoroughly
Perform patch test on arm before neck use
Clean skin and shave if necessary for better contact
Ensure device is fully charged or properly connected
Application Protocol:
Start with lowest intensity setting
Gradually increase to comfortable level
Limit sessions to recommended duration
Move electrodes periodically if using frequently
Post-Use Care:
Clean electrodes after each use
Inspect skin for reactions
Store properly according to instructions
Charge according to manufacturer guidelines
Special Population Considerations
Elderly Users:
Thinner skin requires gentler settings
May have underlying conditions requiring caution
Possibly reduced sensation needing careful monitoring
Often taking medications that might interact
Athletes and Active Users:
May tolerate higher intensities
Should still follow recommended guidelines
Need adequate recovery time between uses
Should complement rather than replace proper training
Office Workers and Sedentary Users:
Good candidates for preventive use
Should maintain proper posture during use
Need to combine with movement and stretching
May benefit from lower intensity settings
Recognizing and Addressing Problems
Warning Signs to Stop Use:
Pain beyond mild discomfort
Muscle spasms that continue after use
Skin burns or persistent irritation
Dizziness or lightheadedness
Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat
What to Do If Problems Occur:
Discontinue use immediately
Consult healthcare provider if symptoms persist
Report adverse events to manufacturer
Contact medical professional for serious reactions
Quality and Counterfeit Concerns
Identifying Safe Devices:
Purchase from reputable retailers
Look for proper certification markings
Check for manufacturer contact information
Read reviews and research brands
Avoiding Dangerous Products:
Be wary of extremely low prices
Avoid devices without safety certifications
Steer clear of products with vague instructions
Don’t use devices with damaged packaging or components
Professional Medical Perspectives
When to Consult a Doctor:
Before use if you have any medical conditions
If you experience persistent side effects
When considering use for specific medical conditions
If unsure about appropriate settings or usage
What Healthcare Providers Recommend:
Start with professional guidance if possible
Use as complement to other treatments
Don’t rely solely on EMS for serious conditions
Combine with traditional physical therapy when appropriate
Comparative Safety: EMS vs Other Modalities
Compared to Manual Therapy:
More consistent pressure application
Less dependent on practitioner skill
Potentially more predictable results
Different risk profile (electrical vs mechanical)
Compared to Medication:
Fewer systemic side effects
No risk of addiction
Immediate discontinuation possible if issues arise
Different mechanism of action
Regulatory Landscape and Standards
United States Regulations:
FDA regulates as medical devices
Classification based on risk level
Manufacturing standards enforcement
Post-market surveillance requirements
International Standards:
CE marking for European market
ISO standards for quality management
Electrical safety certifications
Environmental compliance requirements
Emergency Preparedness and First Aid
Basic First Aid for Problems:
Skin irritation: Clean area, apply soothing cream
Muscle soreness: Rest, gentle stretching, hydration
Burn: Cool water, sterile dressing, medical attention
Serious reaction: Seek immediate medical help
Emergency Contacts:
Poison control for electrical exposure
Emergency services for serious reactions
Manufacturer customer service
Healthcare provider for advice
Conclusion: Balancing Benefits and Risks
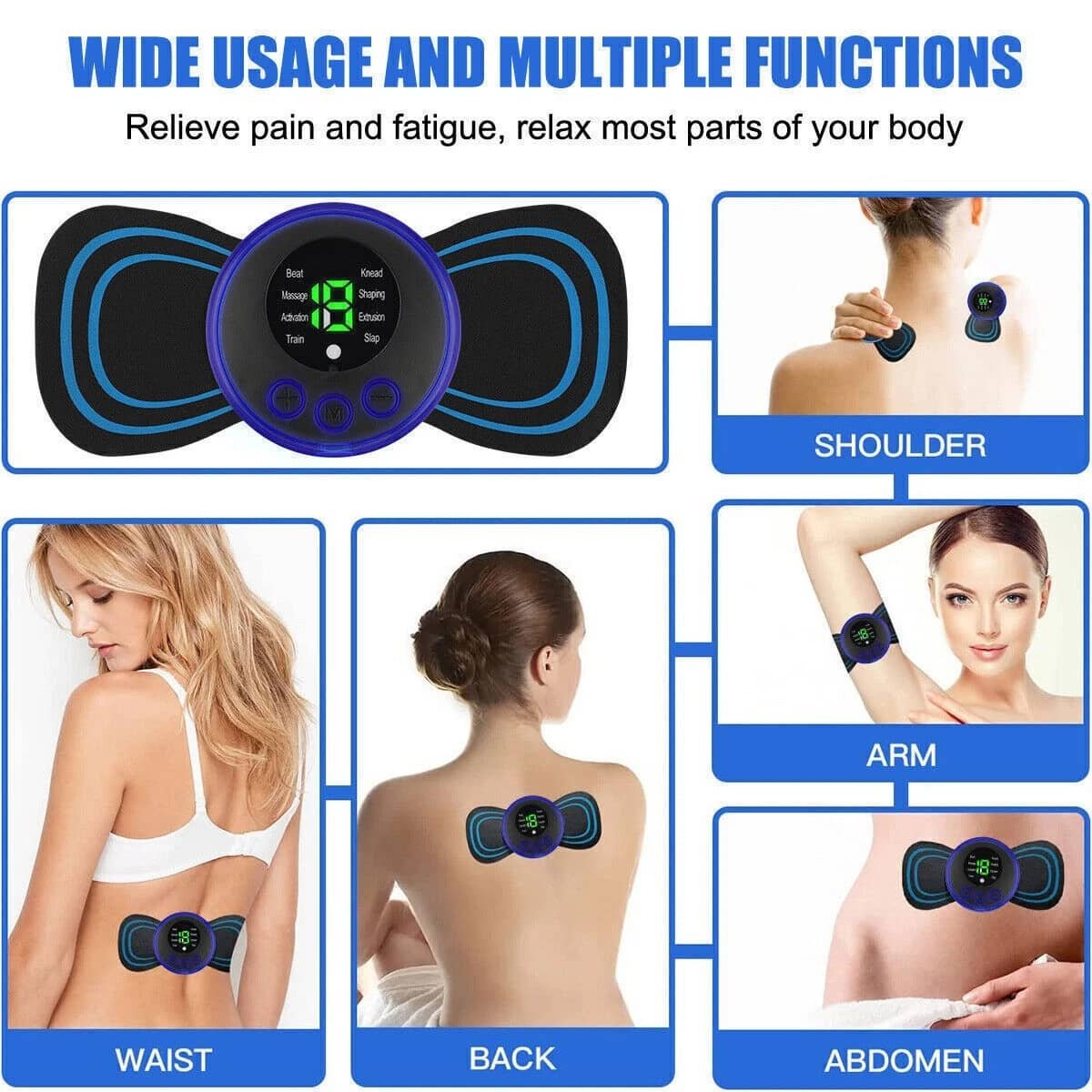 EMS neck massagers are generally safe for most healthy adults when used properly and with appropriate precautions. However, like any therapeutic device, they carry potential risks that must be understood and managed.
EMS neck massagers are generally safe for most healthy adults when used properly and with appropriate precautions. However, like any therapeutic device, they carry potential risks that must be understood and managed.
Key Safety Conclusions:
Generally safe when used as directed by healthy individuals
Multiple contraindications require careful consideration
Quality matters – choose reputable devices with proper certifications
Proper usage is essential for safety and effectiveness
Medical consultation recommended for those with health concerns
Final Recommendations:
Start slowly with low intensity
Follow manufacturer instructions carefully
Listen to your body and stop if anything feels wrong
Consult healthcare providers with any concerns
Use as part of a comprehensive wellness approach
While EMS technology offers promising benefits for neck pain and muscle tension, safety should always be the primary consideration. By understanding the potential risks, following proper usage guidelines, and choosing quality devices, most users can safely enjoy the benefits of EMS neck massagers.
Remember that individual responses may vary, and what works safely for one person may not be appropriate for another. When in doubt, consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that EMS therapy is appropriate for your specific situation and health status.
Related topics:
The Art of Appreciation: Selecting Meaningful Employee Recognition Gifts

